Authentication¶
If you use Databricks configuration profiles or Databricks-specific environment variables for Databricks authentication, the only code required to start working with a Databricks workspace is the following code snippet, which instructs the Databricks SDK for Python to use its default authentication flow:
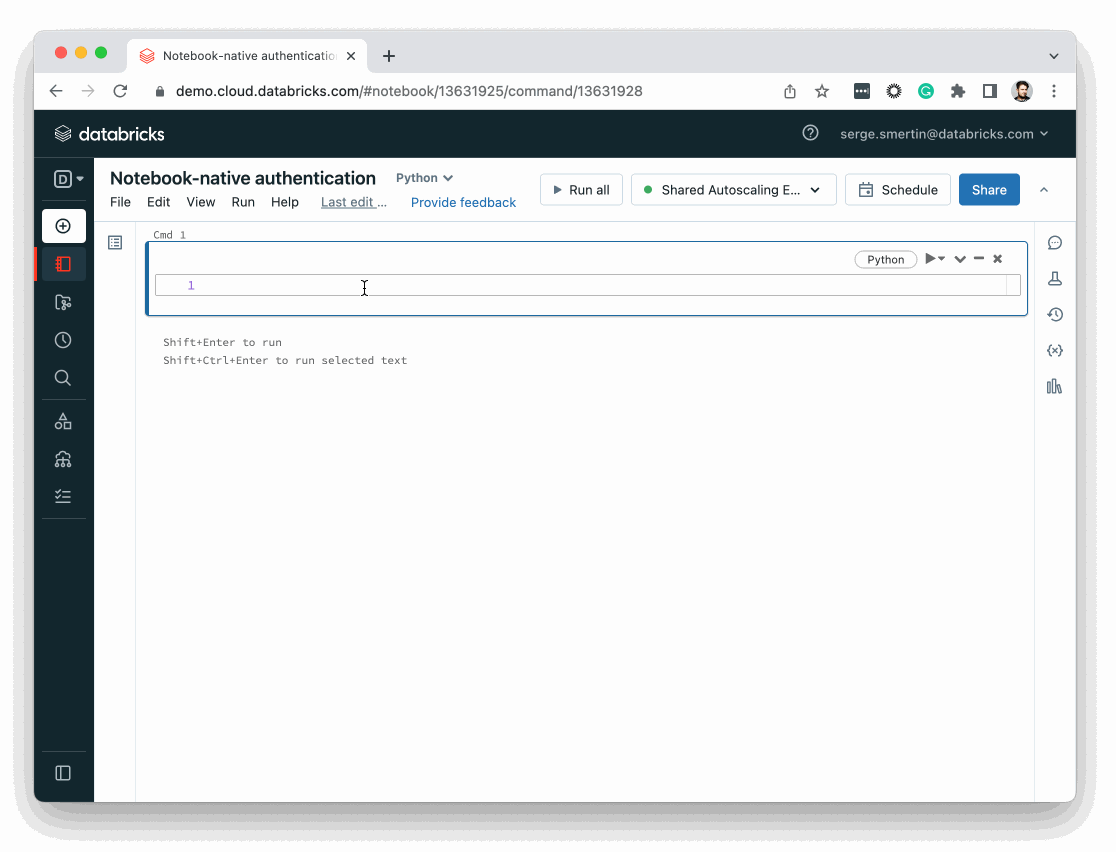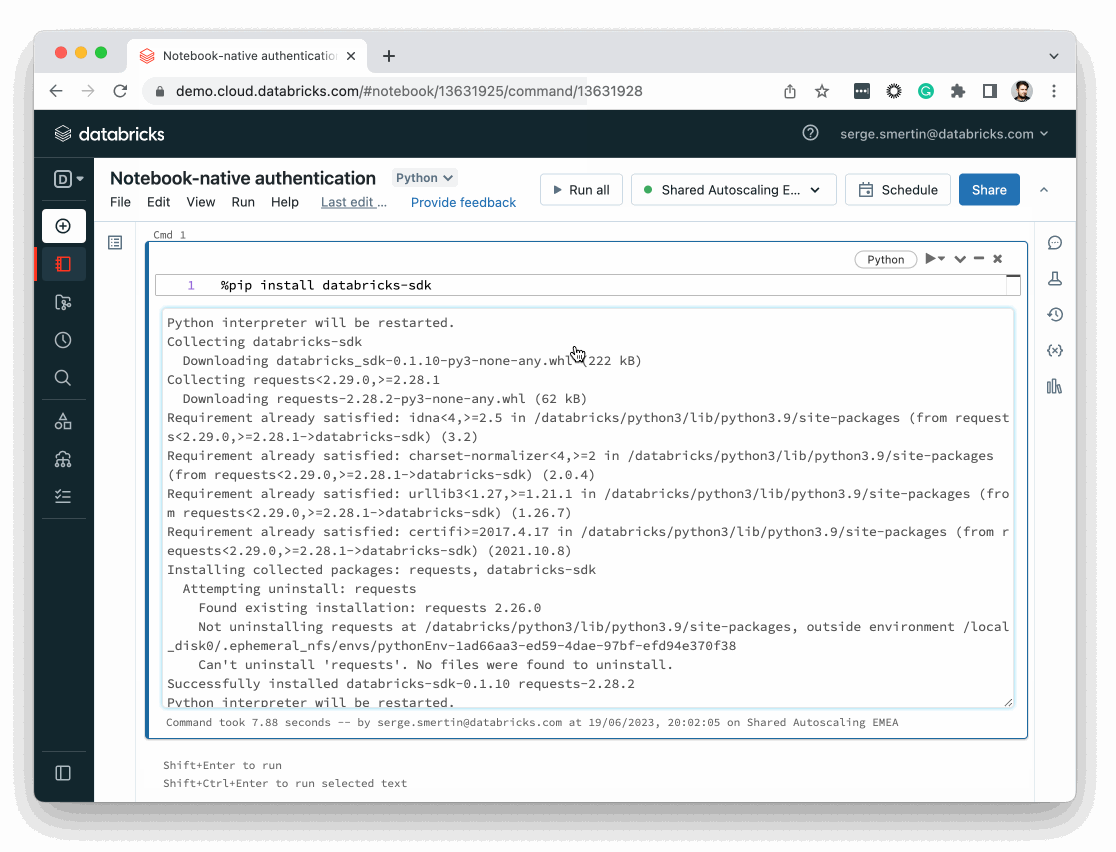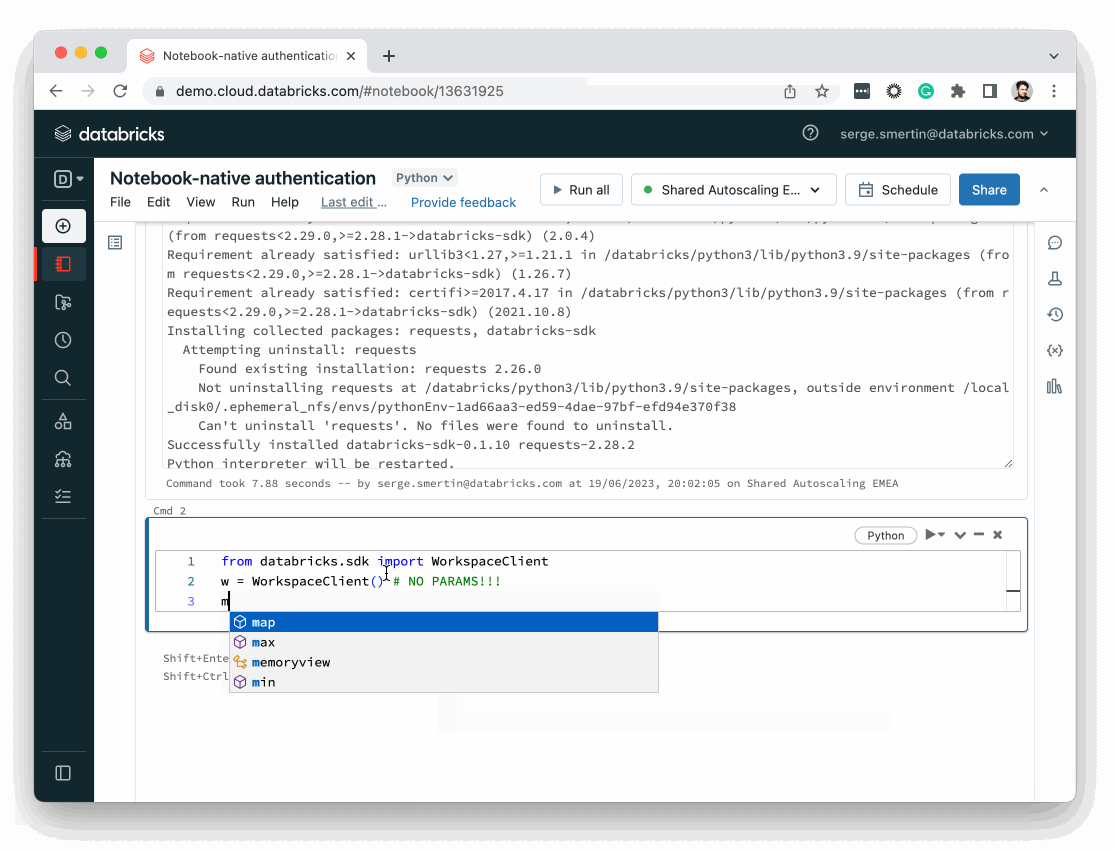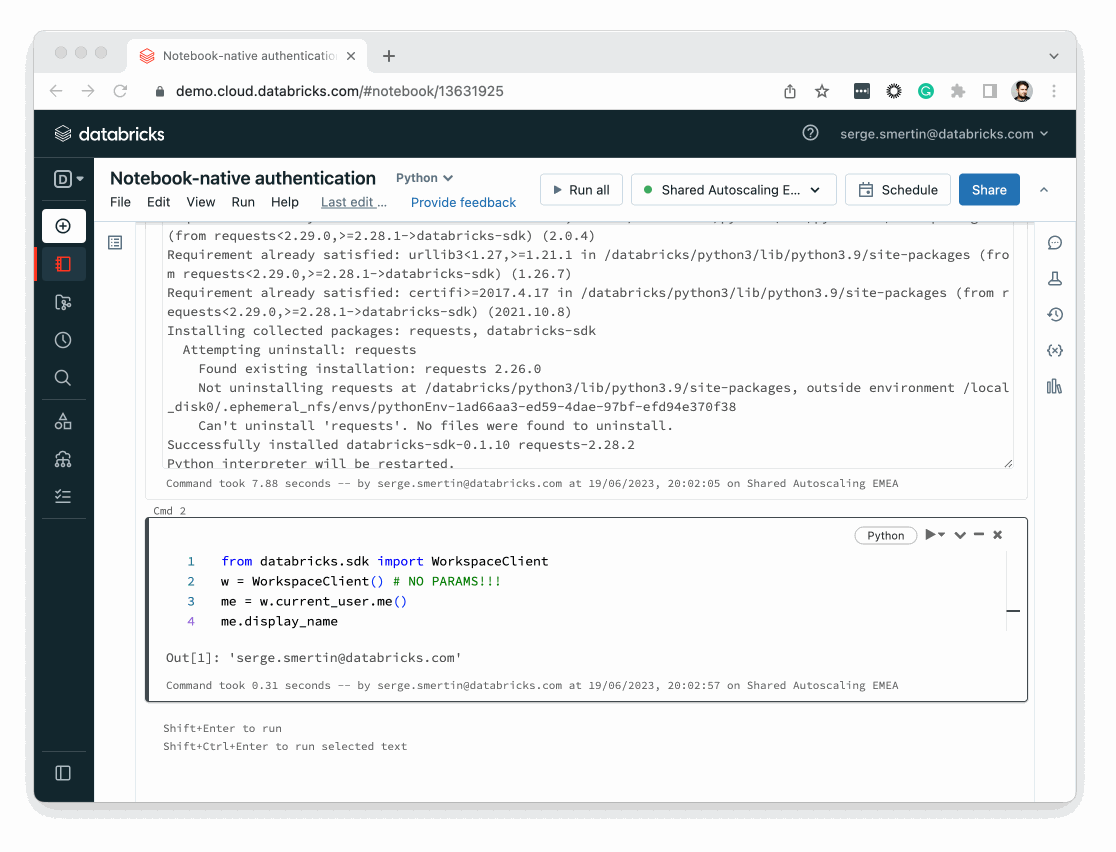
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
w = WorkspaceClient()
w. # press <TAB> for autocompletion
The conventional name for the variable that holds the workspace-level client of the Databricks SDK for Python is w, which is shorthand for workspace.
Notebook-native authentication¶
If you initialise WorkspaceClient without any arguments, credentials will be picked up automatically from the notebook context.
If the same code is run outside the notebook environment, like CI/CD, you have to supply environment variables for the authentication to work.
databricks.sdk.AccountClient does not support notebook-native authentication.
Default authentication flow¶
If you run the Databricks Terraform Provider, the Databricks SDK for Go, the Databricks CLI, or applications that target the Databricks SDKs for other languages, most likely they will all interoperate nicely together. By default, the Databricks SDK for Python tries the following authentication methods, in the following order, until it succeeds:
If the SDK is unsuccessful at this point, it returns an authentication error and stops running.
You can instruct the Databricks SDK for Python to use a specific authentication method by setting the auth_type argument
as described in the following sections.
For each authentication method, the SDK searches for compatible authentication credentials in the following locations, in the following order. Once the SDK finds a compatible set of credentials that it can use, it stops searching:
Credentials that are hard-coded into configuration arguments.
:warning: Caution: Databricks does not recommend hard-coding credentials into arguments, as they can be exposed in plain text in version control systems. Use environment variables or configuration profiles instead.
Credentials in Databricks-specific environment variables.
For Databricks native authentication, credentials in the
.databrickscfgfile’sDEFAULTconfiguration profile from its default file location (~for Linux or macOS, and%USERPROFILE%for Windows).For Azure native authentication, the SDK searches for credentials through the Azure CLI as needed.
Depending on the Databricks authentication method, the SDK uses the following information. Presented are the WorkspaceClient and AccountClient arguments (which have corresponding .databrickscfg file fields), their descriptions, and any corresponding environment variables.
Databricks native authentication¶
By default, the Databricks SDK for Python initially tries Databricks token authentication (auth_type='pat' argument). If the SDK is unsuccessful, it then tries Databricks basic (username/password) authentication (auth_type="basic" argument).
For Databricks token authentication, you must provide
hostandtoken; or their environment variable or.databrickscfgfile field equivalents.For Databricks basic authentication, you must provide
host,username, andpassword(for AWS workspace-level operations); orhost,account_id,username, andpassword(for AWS, Azure, or GCP account-level operations); or their environment variable or.databrickscfgfile field equivalents.
Argument |
Description |
Environment variable |
|---|---|---|
|
(String) The Databricks host URL for either the Databricks workspace endpoint or the Databricks accounts endpoint. |
|
|
(String) The Databricks account ID for the Databricks accounts endpoint. Only has effect when |
|
|
(String) The Databricks personal access token (PAT) (AWS, Azure, and GCP) or Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) token (Azure). |
|
|
(String) The Databricks username part of basic authentication. Only possible when |
|
|
(String) The Databricks password part of basic authentication. Only possible when |
|
For example, to use Databricks token authentication:
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
w = WorkspaceClient(host=input('Databricks Workspace URL: '), token=input('Token: '))
Azure native authentication¶
By default, the Databricks SDK for Python first tries Azure client secret authentication (auth_type='azure-client-secret' argument). If the SDK is unsuccessful, it then tries Azure CLI authentication (auth_type='azure-cli' argument). See Manage service principals.
The Databricks SDK for Python picks up an Azure CLI token, if you’ve previously authenticated as an Azure user by running az login on your machine. See Get Azure AD tokens for users by using the Azure CLI.
To authenticate as an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) service principal, you must provide one of the following. See also Add a service principal to your Azure Databricks account:
azure_workspace_resource_id,azure_client_secret,azure_client_id, andazure_tenant_id; or their environment variable or.databrickscfgfile field equivalents.azure_workspace_resource_idandazure_use_msi; or their environment variable or.databrickscfgfile field equivalents.
Argument |
Description |
Environment variable |
|---|---|---|
|
(String) The Azure Resource Manager ID for the Azure Databricks workspace, which is exchanged for a Databricks host URL. |
|
|
(Boolean) |
|
|
(String) The Azure AD service principal’s client secret. |
|
|
(String) The Azure AD service principal’s application ID. |
|
|
(String) The Azure AD service principal’s tenant ID. |
|
|
(String) The Azure environment type (such as Public, UsGov, China, and Germany) for a specific set of API endpoints. Defaults to |
|
For example, to use Azure client secret authentication:
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
w = WorkspaceClient(host=input('Databricks Workspace URL: '),
azure_workspace_resource_id=input('Azure Resource ID: '),
azure_tenant_id=input('AAD Tenant ID: '),
azure_client_id=input('AAD Client ID: '),
azure_client_secret=input('AAD Client Secret: '))
Overriding .databrickscfg¶
For Databricks native authentication, you can override the default behavior for using .databrickscfg as follows:
Argument |
Description |
Environment variable |
|---|---|---|
|
(String) A connection profile specified within |
|
|
(String) A non-default location of the Databricks CLI credentials file. |
|
For example, to use a profile named MYPROFILE instead of DEFAULT:
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
w = WorkspaceClient(profile='MYPROFILE')
# Now call the Databricks workspace APIs as desired...
Additional configuration options¶
For all authentication methods, you can override the default behavior in client arguments as follows:
Argument |
Description |
Environment variable |
|---|---|---|
|
(String) When multiple auth attributes are available in the environment, use the auth type specified by this argument. This argument also holds the currently selected auth. |
|
|
(Integer) Number of seconds for HTTP timeout. Default is 60. |
(None) |
|
(Integer) Number of seconds to keep retrying HTTP requests. Default is 300 (5 minutes). |
(None) |
|
(Integer) Truncate JSON fields in debug logs above this limit. Default is 96. |
|
|
(Boolean) |
|
|
(Integer) Maximum number of requests per second made to Databricks REST API. |
|
For example, to turn on debug HTTP headers:
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
w = WorkspaceClient(debug_headers=True)
# Now call the Databricks workspace APIs as desired...